Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition affecting approximately 5% of the Irish population, including both children and adults. Effective management of ADHD often involves a combination of behavioral therapies and pharmacological treatments. However, recent shortages of ADHD medications in Ireland have significantly disrupted the lives of those dependent on these treatments. This blog post delves into the causes, impacts, and potential solutions to the ongoing ADHD medication shortages in Ireland.
Understanding the Scope of the Shortage
Between January and August 2024, nearly 20,000 patients in Ireland were prescribed ADHD medication, marking a substantial increase from previous years. This surge in demand has coincided with notable supply chain disruptions. The Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) has reported interruptions in the availability of several ADHD medications, including Tyvense (lisdexamfetamine) and Atomoxetine, due to manufacturing delays and unexpected increases in demand. 
Global Factors Contributing to Local Shortages
The medication shortages in Ireland are not isolated incidents but part of a broader global issue. Manufacturing and supply chain challenges, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, have led to a 30% increase in drug shortages over the past two years. The European Union’s reliance on non-EU countries for pharmaceutical imports, particularly from India and China, has further strained the supply chain. Consolidation of manufacturing sites and leaner global supply chains have reduced resilience, making the system more susceptible to disruptions. 
Impact on Patients and Families
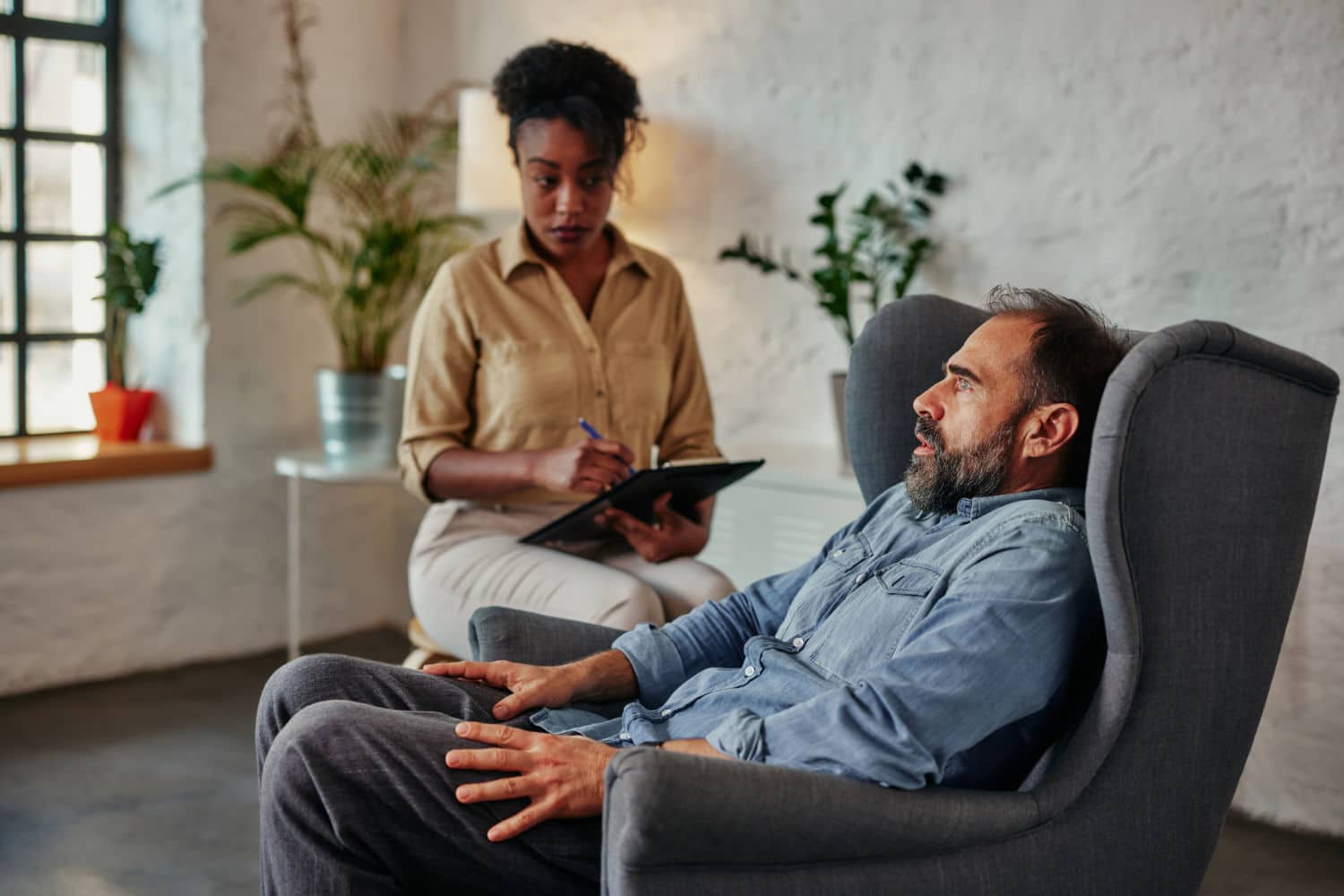
The repercussions of these shortages are profound. Individuals like Paul Barry de Carvalho, diagnosed with ADHD in 2024, have been forced to ration their medication, leading to a resurgence of symptoms such as hyperactivity and lack of focus. Parents of children with ADHD report significant disruptions in education and daily routines due to inconsistent medication availability. The psychological toll of uncertainty and the logistical challenges of sourcing medication have added stress to already burdened families. 
Healthcare System’s Response
In response to the crisis, the HPRA, in collaboration with the Department of Health and the Health Service Executive (HSE), is actively engaging with stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies and wholesalers, to monitor and address the supply issues. Efforts are focused on preempting and mitigating the impacts of shortages. For instance, Takeda, the manufacturer of Tyvense, has communicated expected resupply dates, and alternative strengths of medications are being made available where possible. 
Guidance for Healthcare Professionals
The HSE’s Medicines Management Programme has issued guidance to prescribers on managing medication shortages. Recommendations include prescribing a 28-day supply to prevent exacerbating shortages and consulting with pharmacists to confirm the availability of specific medications. Specialist teams are advised to adjust dosages based on product availability and to consider treatment breaks where clinically appropriate. 
Support Resources for Patients
To assist individuals affected by ADHD, the HSE, in partnership with ADHD Ireland and the UCD School of Psychology, has developed the Adult ADHD App. This application provides information on diagnosis, available medications, psychosocial interventions, and self-help techniques. It serves as a valuable resource for adults diagnosed with ADHD, those who suspect they may have the condition, and their families. 
Looking Forward: Potential Solutions
Addressing the ADHD medication shortage requires a multifaceted approach:
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Reducing dependence on a limited number of manufacturing sites by diversifying production locations can enhance resilience against disruptions.
- Strategic Stockpiling: Establishing reserves of critical medications can buffer against temporary shortages, ensuring continuity of care for patients.
- Policy Interventions: Governmental bodies can implement policies to encourage local production of essential medications and streamline regulatory processes to facilitate quicker responses to shortages.
- Patient Education and Support: Providing patients and families with up-to-date information on medication availability and alternative treatment options can help mitigate anxiety and ensure adherence to treatment plans.
Conclusion
The ADHD medication shortages in Ireland highlight the vulnerabilities within global pharmaceutical supply chains and underscore the critical need for proactive measures to ensure the availability of essential medications. By understanding the contributing factors and implementing strategic solutions, stakeholders can work collaboratively to prevent future shortages and safeguard the well-being of individuals reliant on these treatments.